Everything posted by Mopar1973Man
-
Injector upgrade
Yeap... But its only 180 miles to my local AutoZone in Boise, ID... I might as well stop at Cummins...:confused: The closest thing to me is NAPA which is in Council, ID at 52 miles from me... :eek:
-
4x4 light
Oh No... :eek::ahh: The information I looked up was a 1990 1st gen... Let me move this over to the 24V 2nd Gen stuff... EDIT: Your lucky! The information goes from 1985 to 2002 for CAD axles...
-
Injector upgrade
Well... The local one in Grangeville, ID is well rather more for farm machinery... Not much for the Dodge Cummins... But there is a Cummins dealer in Boise, ID but its 3 hours away... So either way I would have to drive long distance or just order it anyways... I'm in the middle of Nowhere Idaho... The closest town to me has a population of 300 people...:eek:
-
Valve adjustment question
Just for the record I'm going to look it up... http://www.dodgeram.org/tech/dsl/maint/1st_Gen-12v.htm
-
Injector upgrade
Hmmm... Not a bad idea being is was last done at ~95K miles... Hard to tell if its the nasty winterized fuel... Valve Lash... Or the Extreme cold... :confused: Man I'm going buggy looking at these Injection sitting on my desk right next to me... Oh I want to go out and slam in a set of sticks right now and go play... :ahh:
-
4x4 light
Just helps more when I got a yeap and make in the signature... Other than that I got to guess and hope I hit the nail on the head...:ahh:
-
4x4 light
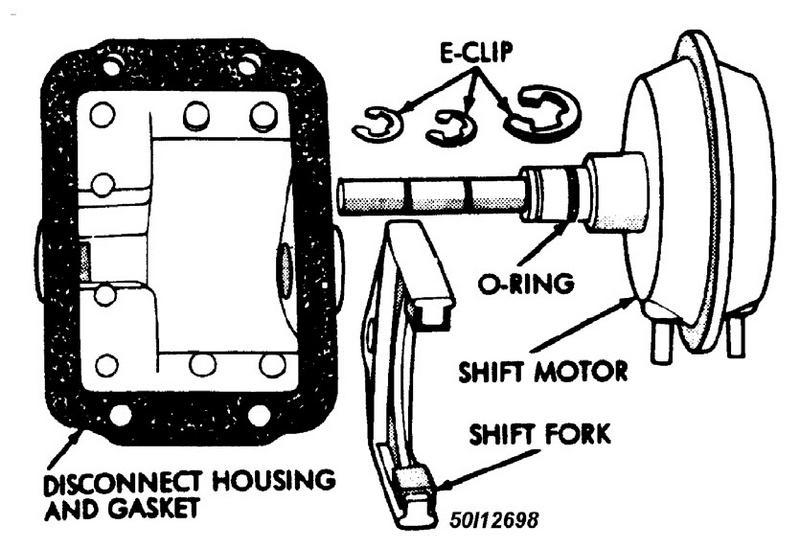
Pulled out my big book... Since I still don't know what year truck I took a guess...:confused: AXLE SHIFT MOTOR FUNCTIONAL TEST 1. Raise and support the vehicle. Disconnect the vacuum harness from the axle shift motor and connect a vacuum pump to the vacuum shift motor front port. See Fig. 2 . 2. Apply 15 in. Hg (51 kPa) of vacuum to the front port and rotate left front wheel to fully disengage the inner and intermediate axle shafts (i.e., shift to two-wheel drive operation). 3. The shift motor should maintain the vacuum applied to the front port for a minimum of 30 seconds. If the motor does not maintain the vacuum, replace it. If the motor does maintain the vacuum, proceed to the next step. 4. Disconnect the vacuum pump from the vacuum shift motor front port. Connect the vacuum pump to the vacuum shift motor rear port, cap the port for the 4WD indicator lamp switch, apply 15 in. Hg (51 kPa) of vacuum to the rear port. 5. The shift motor should maintain the vacuum applied to the rear port for a minimum of 30 seconds. If the shift motor does not maintain the vacuum, replace it. See AXLE SHIFT MOTOR under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. If the motor does maintain the vacuum, proceed to the next step. 6. Remove the cap from the port for the 4WD indicator lamp switch. If vacuum was present, the shift motor is functioning normally. If vacuum was not present, go to next step. 7. Apply 15 in. Hg (51 kPa) of vacuum to the shift motor rear port. Rotate the left front wheel as necessary and ensure that the inner and intermediate axle shafts are completely engaged. The axles must be completely engaged (i.e., shifted to 4WD operation) to open the port for the 4WD indicator lamp switch. 8. Determine if vacuum is present at the port for the 4WD indicator lamp switch again. If vacuum was present at the port, the shift motor is functioning normally. If vacuum was not present at the port, replace the shift motor. See AXLE SHIFT MOTOR under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION. 9. Connect the vacuum harness to the shift motor. See VACUUM HOSE ROUTING . Remove the supports and lower the vehicle. REMOVAL & INSTALLATION - AXLE SHIFT MOTOR Removal 1. Raise and support the vehicle at a comfortable working height. 2. Disconnect the vacuum and wiring connector from the shift housing. 3. Remove the shift motor housing cover, gasket and shield from the housing. 4. Remove the E-clips from the shift motor housing and shaft. Remove shift motor and shift fork from the housing. See Fig. 6 . 5. Remove the O-ring seal from the shift motor shaft. 6. Clean and inspect all the components. If any component is excessively worn or damaged, it should be replaced. http://forum.mopar1973man.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=83&stc=1&d=1260655616 Installation 1. Install a replacement O-ring seal on the shift motor shaft. See Fig. 5 . 2. Insert the shift motor shaft through the hole in the housing and shift fork. The shift fork offset should be toward the differential. 3. Install the E-clips on the shift motor shaft and housing. 4. Install the shift motor housing gasket and cover. Ensure that the shift fork is correctly guided into the shift collar groove. 5. Install the shift motor housing shield and attaching bolts. Tighten the bolts to 10 ft. lbs. (14 Nm).
-
4x4 light
Sorry no... That vacuum can on the CAD unit should twist or turn at all. More that likely there is a vacuum leak and that why its not pulling to lock or unlock position properly...
-
2003 High Idle
I check all through my books and I can seem to find any reference to 3 cylinder high idle in a 3rd Gen... There is no TSB for the flash like the 2nd Gen 24V... :confused:
-
4x4 light
CAD system is a vacuum operated system on the front axle. There is a vacuum diaphram that pulls/push the locking collar on the axle locking into 4WD or returning to 2WD function. But is common for vacuum line damage to causes issues with CAD axles. Non-CAD axles are locked solid all the time. The Transfer case does the locking and unlocking function.
-
4x4 light
Hmmm... Do you have the CAD (Center Axle Discconect) axle in the front? Could you update your signature with information about your truck then I can at least look up information concerning your model and year...
-
Grid heater information
I'll double check my books and see if the same rule applies to the 24V... But from a gut feeling I would say Yes!...
-
Cold weather and timing
No... I'm the one that run around all summer long without grid heater remember? But for the sake of the thread I'll go out and test the voltage on mine...
-
Finally someone telling the truth about EBay!
I was out surfing around the internet... Looking at the different injection pump places and saw this notice box over at Industrial Injection... http://www.industrialinjection.com/ BEWARE of cheap Chinese imitation turbochargers and fuel injection parts sold on EBay and other web sites. They are not built of high quality parts or materials and have high failure rates. These knock-off parts are sold as name brand and under MAP pricing. The parts being sold as new on EBay or other auction web sites are not Industrial Injection products. Industrial Injection sells ONLY genuine original products.
-
Cold weather and timing
Sureeeee, make me go out and test the voltage why don't you!
-
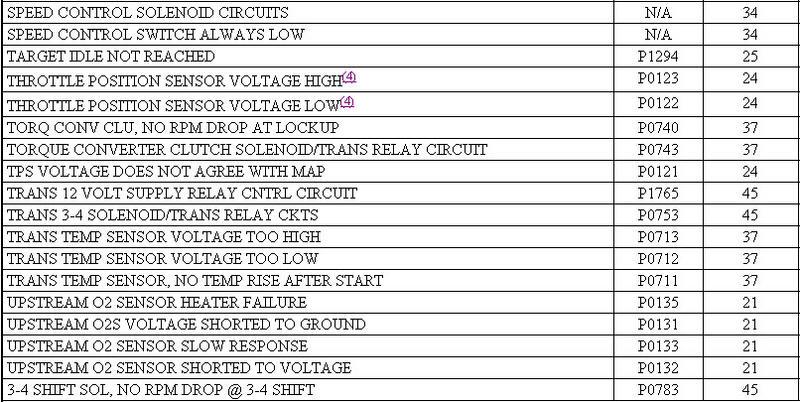
Error Code Retrieval
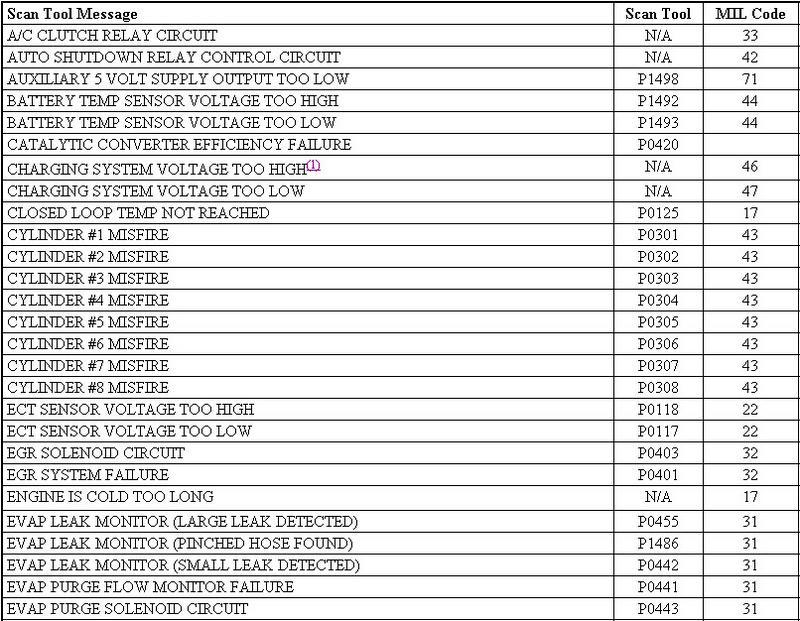
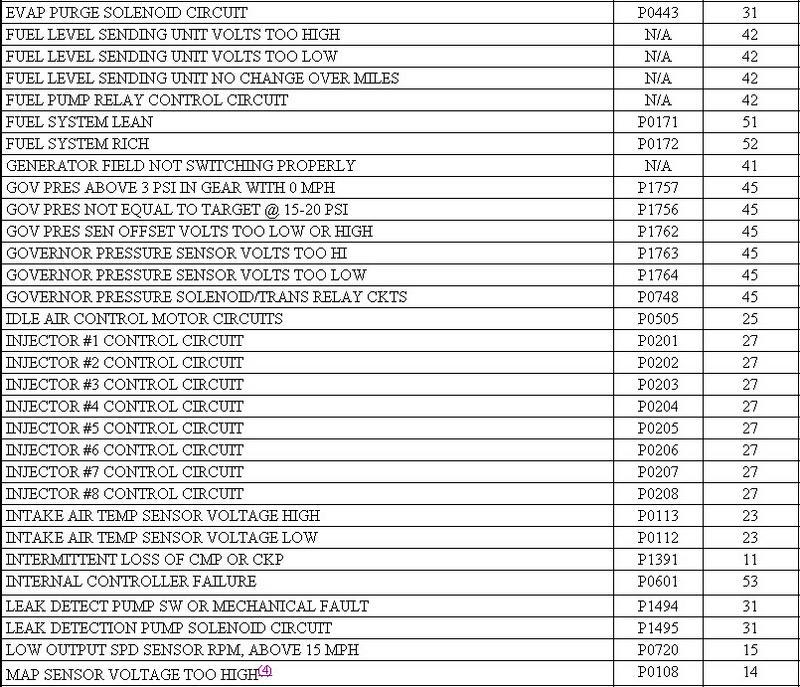
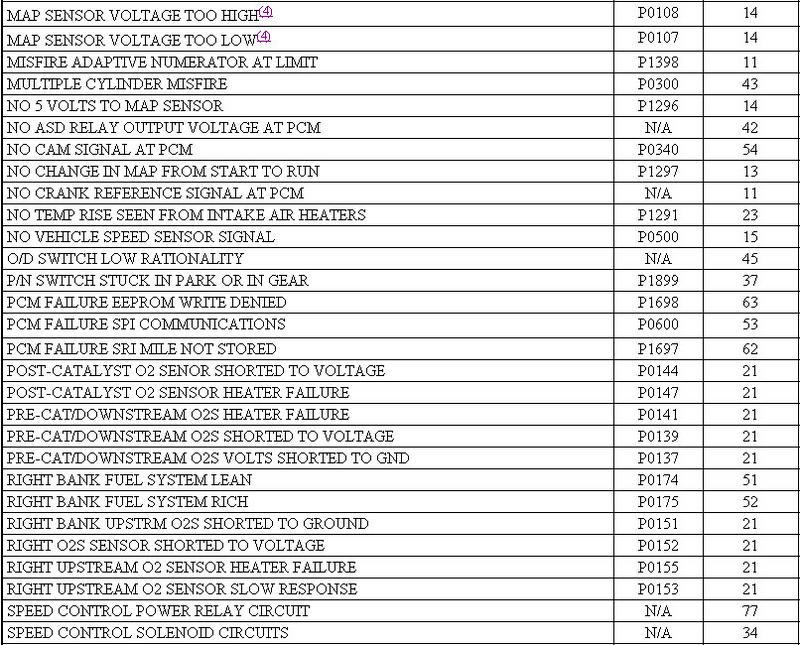
Using Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) 1. Ensure battery is fully charged. Turn ignition on and note operation of MIL. When ignition is first turned on, MIL should come on and remain on for 3 seconds to verify bulb and circuit operation, and then go off. 2. Attempt to start engine. Turn ignition off. Without starting engine, turn ignition on, off, on, off and on within 5 seconds. Record 2-digit DTCs as displayed by flashing MIL. 3. For example, DTC 24 will be displayed by 2 flashes, short pause, and then 4 more flashes. A short pause will exist between first and second digits on DTC. If more than one DTC is stored, after first DTC is displayed, there will be a longer pause and then another stored DTC will be displayed. 4. Once all DTCs are recorded, retrieve DTCs using scan tool to ensure all DTCs are obtained. See USING SCAN TOOL. Using Scan Tool 1. Ensure battery is fully charged. Attempt to start engine. Turn ignition off. Connect scan tool to Data Link Connector (DLC). DLC is located below instrument panel near steering column. 2. Turn ignition on. Using scan tool manufacturer's instructions, record all DTCs displayed on scan tool. Using all DTCs obtained, proceed to SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TESTS . Once all repairs are made, ensure DTCs are cleared from PCM memory. See CLEARING DTCS. http://forum.mopar1973man.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=74&stc=1&d=1260588746 http://forum.mopar1973man.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=78&stc=1&d=1260589692 http://forum.mopar1973man.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=79&stc=1&d=1260589692 http://forum.mopar1973man.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=80&stc=1&d=1260589692 ........................................................................................................ P0783 - 45
-
Stalls when going into gear
Ok after pulling out the big book and doing some reading on this... As for the specs on the TQ converter I don't have any you might have to contact a trans shop and get that information... Drags Or Locks Up Check for low fluid level, dragging or failed clutch, improper front or rear band adjustment, internal transmission case leaks, servo band or linkage malfunction, worn overrunning clutch, broken planetary gears or dragging torque converter clutch. TORQUE CONVERTER CAUTION: Torque converter is a welded assembly and is not serviceable. If a malfunction occurs or if torque converter becomes contaminated with foreign material, it MUST be replaced. Torque converter cannot be flushed or repaired. CAUTION: DO NOT open throttle to wide open position for more than 5 seconds or transmission may be damaged. If performing more than one torque converter stall speed test, operate engine at 1000 RPM with transmission in Neutral for at least one minute to cool transmission fluid before performing next torque converter stall speed test. Stall Speed Test 1. Install tachometer. Ensure transmission fluid level is correct. Start and operate engine until transmission fluid is at normal operating temperature. 2. Block front wheels. Apply parking and service brakes. Place transmission in Drive. Open throttle to wide open position for no more than 5 seconds and note engine RPM, then release throttle. This is the torque converter stall speed. 3. Torque converter stall speed should be 1800-2300 RPM. Once torque converter stall speed is obtained, place transmission in Neutral. Operate engine for one minute, allowing transmission to cool. Stop engine. Place transmission in Park. Remove tachometer. Stall Speed Exceeds Specification If torque converter stall speed exceeds specification by more than 200 RPM, transmission clutch is slipping. Stall Speed Less Than Specification 1. If torque converter stall speed is less than specification with a properly tuned engine, torque converter overrunning clutch may be slipping. 2. If torque converter overrunning clutch is slipping, torque converter stall speed will be 250-350 RPM less than the specification. Vehicle will operate properly at highway speeds, but will have poor low-speed acceleration. Stall Speed Is Within Specification If torque converter stall speed is within specification, but abnormal throttle opening is required to maintain highway speeds, torque converter overrunning clutch is seized. Torque converter must be replaced.
-
P1693 codes (SOLO)
NO RESPONSE FROM ENGINE CONTROL MODULE Testing 1. Turn ignition on. Using DRBIII® scan tool, attempt to communicate with Powertrain Control Module (PCM). If scan tool communicates with PCM, go to next step. If scan tool does not communicate with PCM, go to NO RESPONSE FROM ENGINE CONTROL MODULE & POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE . 2. Turn ignition off. Check power and grounds for Engine Control Module (ECM). See CHECKING ENGINE CONTROL MODULE POWER & GROUND CIRCUITS under DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUIT CHECK. Repair as necessary. If power and grounds for ECM are okay, go to next step. 3. Ensure ignition is off. Disconnect ECM harness connector. ECM is located on driver's side of engine, just in front of fuel transfer pump and contains a 50-pin connector. Disconnect scan tool from Data Link Connector (DLC). Using DVOM, measure resistance between ground and terminal No. 39 (Dark Green wire) on ECM harness connector. If resistance is 5 ohms or greater, go to next step. If resistance is less than 5 ohms, repair short to ground in Dark Green wire. 4. Ensure ignition is off. Using DVOM, measure resistance of Dark Green wire between terminal No. 39 on ECM harness connector and terminal No. 6 on DLC. If resistance is less than 5 ohms, go to next step. If resistance is 5 ohms or greater, repair open in Dark Green wire. 5. Ensure ignition is off. Using DVOM, measure resistance of Pink/Dark Blue wire between terminal No. 38 on ECM harness connector and terminal No. 7 on DLC. If resistance is less than 5 ohms, go to next step. If resistance is 5 ohms or greater, repair open in Pink/Dark Blue wire. 6. Replace and program the ECM. NO RESPONSE FROM POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE Testing 1. Turn ignition on. Using DRBIII® scan tool, attempt to communicate with Engine Control Module (ECM). ECM may also be referred to as Cummins Controller. If scan tool communicates with ECM, go to next step. If scan tool does not communicate with ECM, go to NO RESPONSE FROM ENGINE CONTROL MODULE & POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE . 2. Turn ignition off. Check power and grounds for Powertrain Control Module (PCM). See CHECKING POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE POWER & GROUND CIRCUITS under DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUIT CHECK. Repair as necessary. If power and grounds for PCM are okay, go to next step. 3. Ensure ignition is off. Disconnect Gray 32-pin PCM harness connector C3. Disconnect scan tool from Data Link Connector (DLC). Using DVOM, measure resistance between ground and terminal No. 29 (White/Violet wire) on PCM harness connector C3. If resistance is 5 ohms or greater, go to next step. If resistance is less than 5 ohms, repair short to ground in White/Violet wire. 4. Ensure ignition is off. Ensure Gray 32-pin PCM harness connector C3 is still disconnected. Using DVOM, measure resistance of White/Violet wire between terminal No. 29 on PCM harness connector C3 and terminal No. 14 on DLC. If resistance is less than 5 ohms, go to next step. If resistance is 5 ohms or greater, repair open in White/Violet wire. 5. Ensure ignition is off. Ensure Gray 32-pin PCM harness connector C3 is still disconnected. Using DVOM, measure resistance of Pink/Dark Blue wire between terminal No. 27 on PCM harness connector C3 and terminal No. 7 on DLC. If resistance is less than 5 ohms, go to next step. If resistance is 5 ohms or greater, repair open in Pink/Dark Blue wire. 6. Replace and program the PCM. NO RESPONSE FROM ENGINE CONTROL MODULE & POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE Testing 1. Turn ignition off. Check power and grounds for Engine Control Module (ECM) and Powertrain Control Module (PCM). See DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUIT CHECK . Repair as necessary. If power and grounds for ECM and PCM are okay, go to next step. 2. Ensure ignition is off. Reconnect all disconnected components. Disconnect PCM harness connectors. Turn ignition on. Using DRBIII® scan tool, attempt to communicate with ECM. If scan tool does not communicate with ECM, go to next step. If scan tool communicates with ECM, replace and program the PCM. See appropriate REMOVAL, OVERHAUL & INSTALLATION article. 3. Turn ignition off. Ensure PCM harness connectors are still disconnected. Disconnect scan tool. Disconnect ECM harness connector. Turn ignition on. Using DVOM, measure voltage between ground and terminal No. 7 (Pink/Dark Blue wire) on Data Link Connector (DLC). If voltage is one volt or less, go to next step. If voltage is greater than one volt, repair short to voltage in Pink/Dark Blue wire. 4. Turn ignition off. Ensure scan tool, ECM and PCM are still disconnected. Using a DVOM, measure resistance between terminal No. 7 (Pink/Dark Blue wire) and terminals No. 6 (Dark Green wire) and No. 14 (White/Violet wire) on DLC. If resistance is 5 ohms or greater on both measurements, go to next step. If resistance at either measurement is less than 5 ohms, repair short between SCI transmit circuit and appropriate SCI receive circuit that indicated less than 5 ohms. 5. Ensure ignition is off. Ensure scan tool, ECM and PCM are still disconnected. Using a DVOM, measure resistance between ground and terminal No. 7 (Pink/Dark Blue wire) on DLC. If resistance is 5 ohms or greater, go to next step. If resistance is less than 5 ohms, repair short to ground in Pink/Dark Blue wire. 6. Ensure ignition is off. Ensure scan tool, ECM and PCM are still disconnected. Using DVOM, measure resistance of Pink/Dark Blue wire between terminal No. 38 on ECM harness connector and terminal No. 7 on DLC. If resistance is less than 5 ohms, go to next step. If resistance is 5 ohms or greater, repair open in Pink/Dark Blue wire. 7. Ensure ignition is off. Ensure scan tool is disconnected. Disconnect negative battery cable. Using DVOM, measure resistance between ground and terminals No. 4 (Black/Light Green wire) and No. 5 (Black/Tan wire) at DLC. If resistance is less than 5 ohms on both measurements, go to next step. If resistance at either terminal is 5 ohms or greater, repair open in appropriate ground circuit that indicated 5 ohms or greater. 8. Replace and program the ECM.
-
Grid heater information
I know several people have asked about grid heater times and when it starts... Well here you go... GRID HEATERS Above 59*F ........................ 0 Seconds ............................ No Post Heating 15*F to 59*F ...................... 10 Seconds .......................... Post Heating 0*F to 15*F ........................ 15 Seconds ......................... Post Heating Below 0*F ........................... 30 Seconds ......................... Post Heating Remember block heaters tend to offset the intake air temp so be aware that block heater will do this. Also be aware that there is 2 grid heaters and during the pre-heating both elements are used during the post heating it might be 1 or 2 depending on temp at the IAT. Now each grid heater is 95 AMPs a piece for a total of 190 AMPs total draw so this is why is so critical that your batteries are strong in the winter time!
-
Cold weather and timing
Still a bit stuborn at twisting over... I noticed you battery voltage is quite low during the grid heater cycle...:eek:
-
How to pull error codes and the error code list
CHECK ENGINE Light Diagnostic Mode 1. Start engine (if possible). Move transmission shift lever through all gear positions, ending in Park. Turn A/C switch on, then off (if equipped). 2. Turn engine off. Without starting engine again, turn ignition on, off, on, off, and on. Record 2-digit fault codes as displayed by the flashing CHECK ENGINE light. 3. For example, Code 23 is displayed as flash, flash, 4-second pause, flash, flash, flash. After a slightly longer pause, other codes stored are displayed in numerical order. 4. Once CHECK ENGINE light begins to flash fault codes, it cannot be stopped. If you lose count, it will be necessary to start over. Code 55 indicates end of fault code display. 5. Refer to FAULT CODES table to translate fault code number to a system fault description. ERROR CODE LIST 11 NO REFERENCE SIGNAL DURING CRANKING No Reference Signal From Crankshaft Position Sensor Picked Up During Cranking. 15 NO VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL No Distance Sensor Signal Detected With Road Load Conditions. 22 COOLANT SENSOR VOLTAGE TOO LOW Coolant Temp. Sensor Input Less Than Minimum Acceptable Voltage. 22 COOLANT SENSOR VOLTAGE TOO HIGH Coolant Temp. Sensor Input More Than Maximum Acceptable Voltage. 23 CHARGE TEMP VOLT LOW Charge Temp. Sensor Input Less Than Minimum Acceptable Voltage. 23 CHARGE TEMP VOLT HI Charge Temp. Sensor Input More Than Maximum Acceptable Voltage. 24 TPS VOLTAGE LOW TPS Sensor Input Less Than Minimum Acceptable Voltage. 24 TPS VOLTAGE HIGH TPS Sensor Input More Than Maximum Acceptable Voltage. 33 A/C CLUTCH RELAY CKT Open Or Shorted Condition Detected In A/C Clutch Relay Circuit. 34 S/C SOLENOIDS CKT Open Or Shorted Condition Detected In Speed Control (S/C) Vacuum Or Vent Solenoid Circuits. 41 ALTERNATOR FIELD An Open Or Shorted Condition Detected In Alternator Field Ckt. 42 ASD RELAY CIRCUIT An Open Or Shorted Condition Detected In ASD Relay Circuit 42 NO ASD RELAYVOLTAGE SENSED AT SBEC No ASD Relay Voltage Sensed When ASD Relay Is Energized. 45 OVERDRIVE SOLENOID An Open Or Shorted Condition Detected In Overdrive Solenoid Ckt. 46 CHARGING VOLTAGE TOO HIGH Battery Voltage Sense Input More Than Target Charging Voltage During Engine Operation. 47 CHARGING VOLTAGE TOO LOW Battery Voltage Sense Input Less Than Target Charging Voltage During Engine Operation And No Significant Change In Voltage Detected During Active Test Of Alternator Output. 62 EMR MILES NOT STORED Unsuccessful Attempt To Update EMR Mileage In SBEC EEPROMs 63 SBEC FAILURE EEPROM WRITE DENIED Unsuccessful Attempt To Write To An EEPROM Location By SBEC.
-
Preliminary inspection
1. Ensure battery connections are tight and not corroded. Ensure 60-pin connector on Single Board Engine Controller (SBEC) is fully engaged and retaining screw is tight. Check for pushed-out connectors and bent terminals. SBEC is located in left front corner of engine compartment, near horns on left fender. 2. Ensure electrical connections on intake manifold heater relays are tight and not corroded. Intake manifold heater relays are mounted on inner wheelwell. 3. Check for loose or defective electrical connections on starter motor. Ensure electrical connections are installed on charge air temperature sensor and air temperature switch and wiring is okay. Charge air temperature sensor and air temperature switch are located in intake manifold cover. 4. Check for loose or defective electrical connection on engine speed sensor. Engine speed sensor is located on front of engine. Ensure electrical connector is installed on water-in-fuel sensor. Water-in-fuel sensor is located in bottom of fuel/water separator filter. 5. Ensure electrical connection is installed on shutoff solenoid valve and KSB valve on fuel injection pump. 6. Check for tightness and corrosion on electrical connections on intake manifold heater. Intake manifold heater is a grid heater installed between air inlet housing and intake manifold. Air inlet housing is attached to intercooler outlet duct, which is connected to intercooler, located in front of radiator. 7. Check for binding throttle linkage and defective throttle return spring. Ensure ground cable, located near alternator, is tight. Check for leaking fuel lines. 8. Check air filter for restriction and damage. Ensure intercooler inlet and outlet duct clamps are tight.
-
Book and information...
I know a bunch of you are looking for books for your trucks I'm going to list the source of the books I know and were to get them... PDFTown.Com http://pdftown.com/Pdf-eBook/Dodge.html Or check here too... http://forum.mopar1973man.com/downloads.php?do=cat&id=2
-
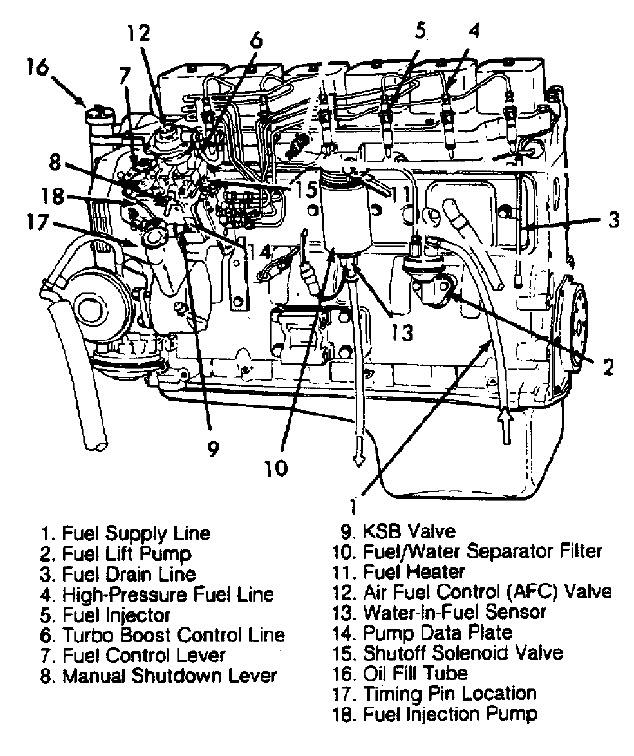
Engine Layout of the 1st Gen
Here you go gang... The engine layout of the 12V VE Pumped Cummins engine... I know the image is a bit poor but its better than nothing... http://forum.mopar1973man.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=71&stc=1&d=1260577188
-
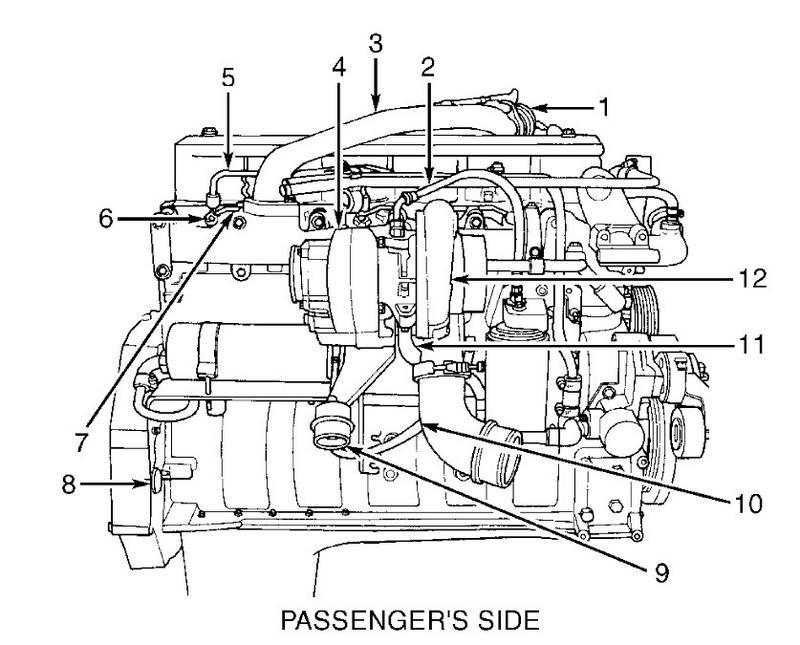
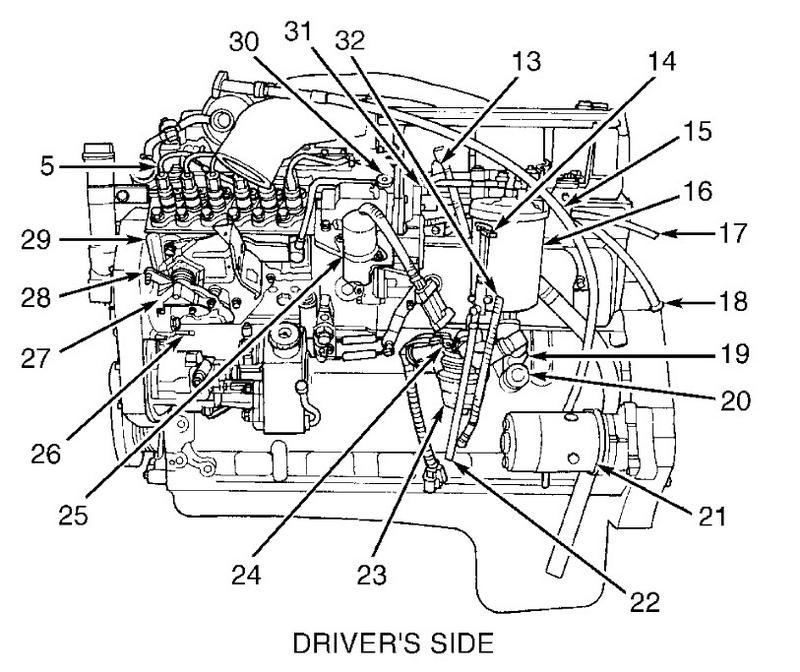
12V Part layout of the engine
Here you go gang 12V layout of both sides of the engine... :thumbsup: http://forum.mopar1973man.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=68&stc=1&d=1260576366 http://forum.mopar1973man.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=69&stc=1&d=1260576366 http://forum.mopar1973man.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=70&stc=1&d=1260576366